숫자 짝꿍 문제는 다음과 같다.
문제와 예시

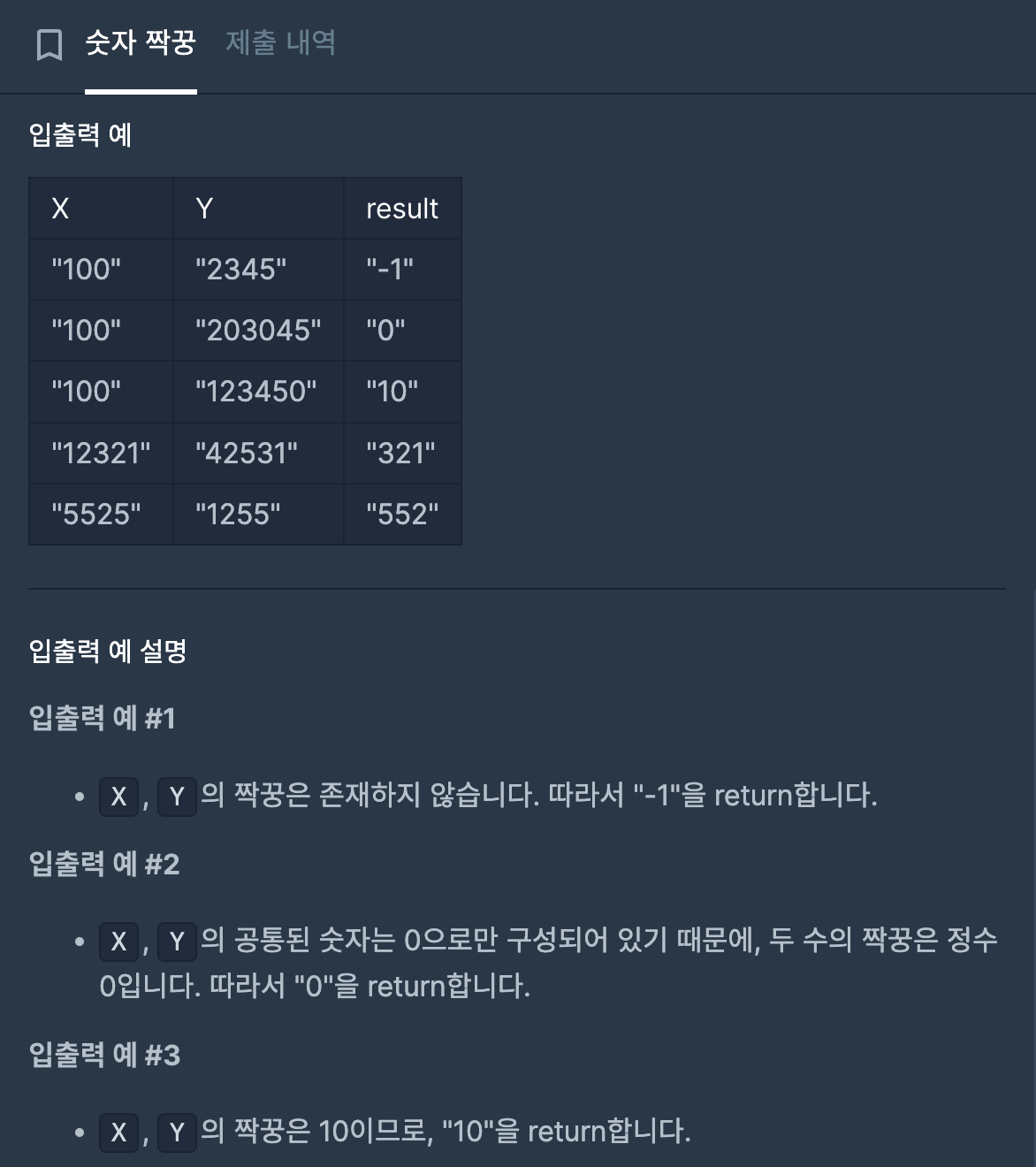

함정이 많아 시간이 생각보다 많이 걸렸고 시간초과 등의 에러가 발생하여
타 풀이를 참조하여 풀었다.
🤓 코드 설계
1. x,y를 int로 치환하기
2. 이중 for문을 돌려서 동일한 값 PriorityQueue에 넣어 반환하기
🤨 구현한 코드 (복잡한 로그 주의⛔️)
package ImplementationAlgorithm;
//
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.management.LockInfo;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String X = "100";
String Y = "123450";
String answer = "";
// transform to digits
int[] digitX = Stream.of(X.split("")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
int[] digitY = Stream.of(Y.split("")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQ = new PriorityQueue<>();
int count = 0;
if(digitX.length>=digitY.length) {
for(int i=0; i< digitX.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j< digitY.length; j++) {
if(digitX[i] == digitY[j]) {
pQ.offer(digitY[j]);
if(pQ.contains(digitY[j])){
count++;
if(count==3){
pQ.remove(digitY[j]);
}
}
}
}
}
} else {
for(int i=0; i< digitY.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j< digitX.length; j++) {
if(digitY[i] == digitX[j]) {
pQ.offer(digitX[j]);
if(pQ.contains(digitX[j])){
count++;
if(count==3){
pQ.remove(digitX[j]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("pQ = " + pQ);
if(pQ.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("-1");
} else if(pQ.poll()==0) {
System.out.println("0");
} else {
System.out.println("pQ = " + pQ);
}
}
}
내 코드의 문제점은
1. 짝꿍이라는 것을 인식하지 않고 동일한 값을 Queue에 넣은 것이 컸다.
짝수라는 핵심 키워드를 고려하지 않고 막무가내로 코드를 짠 것이 화근이었다.
답은 답대로 틀려서 짱구를 굴리다가 40분이 경과하여 chatGPT와 씨름을 해보기 시작하였다.
내가 만든 풀이로 디벨롭 시키고 싶었으나 GPT가 우선순위큐는 효율적이지 않다는 팩폭에 꼬리를 내렸다.
😎 chatGPT의 풀이
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String X, String Y) {
// Transform to digits
int[] digitX = X.chars().map(Character::getNumericValue).toArray();
int[] digitY = Y.chars().map(Character::getNumericValue).toArray();
// Sort digits in descending order
Arrays.sort(digitX);
Arrays.sort(digitY);
int i = digitX.length - 1;
int j = digitY.length - 1;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// Find common digits in descending order
while (i >= 0 && j >= 0) {
if (digitX[i] == digitY[j]) {
sb.insert(0, digitX[i]); // Add digit to the front
i--;
j--;
} else if (digitX[i] > digitY[j]) {
i--;
} else {
j--;
}
}
// If no common digit found, return -1
if (sb.length() == 0) {
return "-1";
}
// If common digit is only 0, return 0
if (sb.toString().replaceAll("0", "").isEmpty()) {
return "0";
}
// Return the result
return sb.reverse().toString();
}
}
주목할 점은
1. StringBuilder를 사용하여 시간 단축
2. for문에서 i--로 최댓값을 구하면 sb.insert()로 넣었다는 점
그럼에도 불구하고 시간초과가 났다.
조금 더 최적화된 코드를 고민하던 중 HashMap을 사용하여 동일한 값을 value에 넣어 카운팅 하는 방법을 택했다.
😯 수정한 코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String X, String Y) {
// Count frequency of digits in X
HashMap<Character, Integer> digitCountX = new HashMap<>();
for (char digit : X.toCharArray()) {
digitCountX.put(digit, digitCountX.getOrDefault(digit, 0) + 1);
}
ArrayList<Character> commonDigits = new ArrayList<>();
// Find common digits
for (char digit : Y.toCharArray()) {
if (digitCountX.containsKey(digit) && digitCountX.get(digit) > 0) {
commonDigits.add(digit);
digitCountX.put(digit, digitCountX.get(digit) - 1);
}
}
// If no common digit found, return -1
if (commonDigits.isEmpty()) {
return "-1";
}
// Sort common digits in descending order
Collections.sort(commonDigits, Collections.reverseOrder());
// If common digit is only 0, return 0
if (commonDigits.size() >= 1 && commonDigits.get(0) == '0') {
return "0";
}
// Construct result string
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char digit : commonDigits) {
sb.append(digit);
}
// Return the result
return sb.toString();
}
}
해시맵을 제대로 사용한 적은 처음이기에 여러 시도를 해보았는데
이번 문제와 같이 키와 값으로 빠르게 검색할 때 유용함을 알게 되었다.
[할 것]
자료구조를 하나둘씩 배워가며 각 기능들이 헷갈리기 시작했다.
최대한 블로그에 적어서 장기메모리로 발전시켜야겠다.